Clean & Debride
Removing any devitalized tissue and slough enables a clearer image of the wound, reducing bioburden, and prepares the wound bed to be staged for further treatment. Thurough wound cleansing and debridement are the foundations that can enable further wound treatments that can aid in the promtion of healing.
Hydrogel
Necrotic tissue or fibrin coatings often prevent or delay healing in chronic wounds. Hydrogels offer an effective moisture balance which aids in the promotion of moist wound healing, but also provides a cleansing effect, which aids in the promotion of autolytic debridement.
Cutimed® Gel
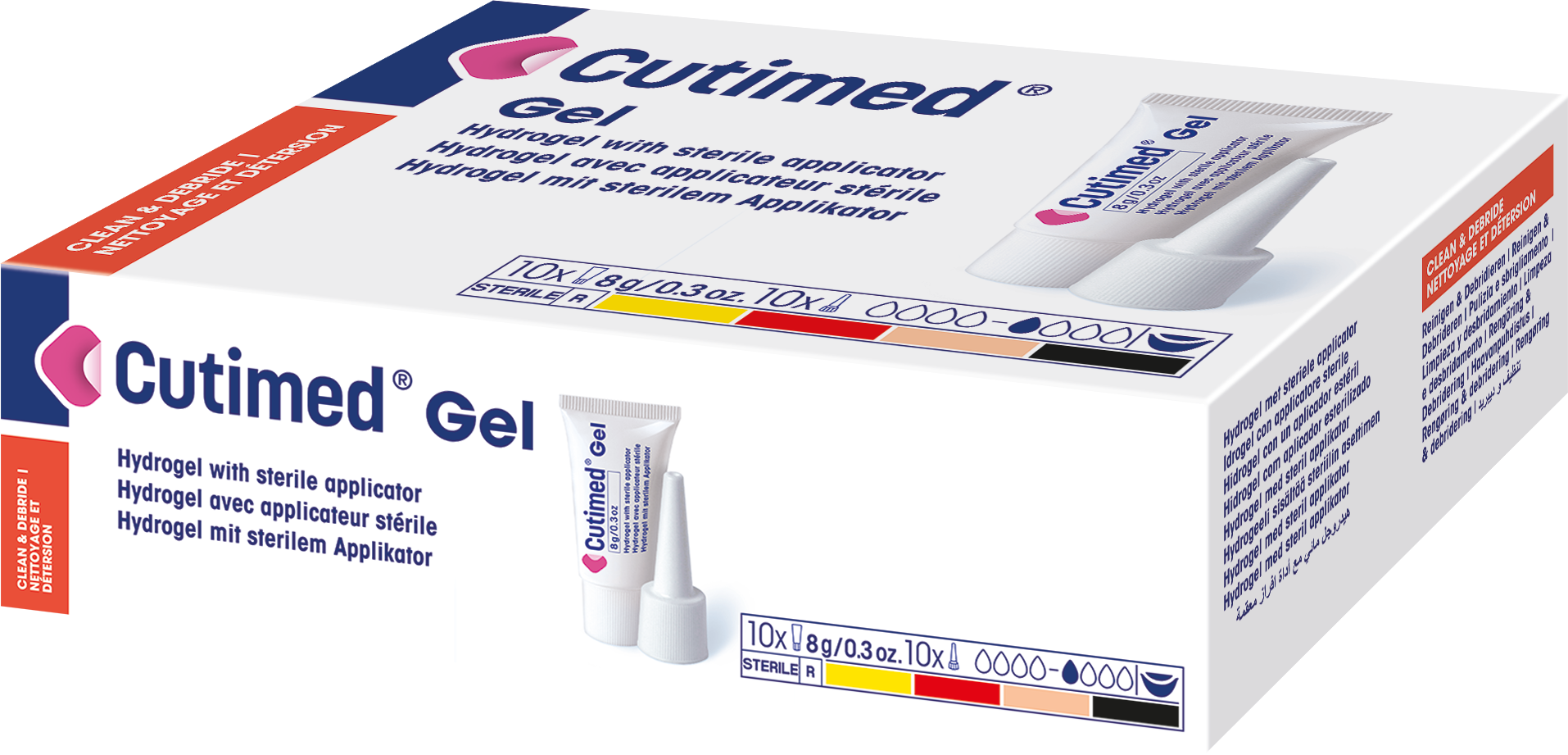
Cutimed® Gel
is a hydrogel with sterile applicator
Manage Infection
Infection is the single likeliest cause of delayed healing in chronic wounds. If neglected, it may escalate to systemic infection or sepsis, which can be life-threatening. Management and prevention of wound infection may lower the use of antibiotics and form a valuable part of your Antimicrobial Stewardship strategy. Cutimed® Sorbact® provides solutions which manage infection to support clinical needs.
Hydrophobic bacteria binding dressings
Cutimed® Sorbact® is an innovation with proven success in infection management. The DACC™-coated surface of Cutimed® Sorbact® has special characteristics and hydrophobic properties that manage and treat infection without releasing active substances into the wound. Hydrophobic bacteria bind and anchor irreversibly to the dressing surface. Utilizing a physical mode of action, Sorbact® safely Binds-Inhibits-Removes hydrophobic bacteria from the wound without leaving any active substances in the wound.
Cutimed® Sorbact®
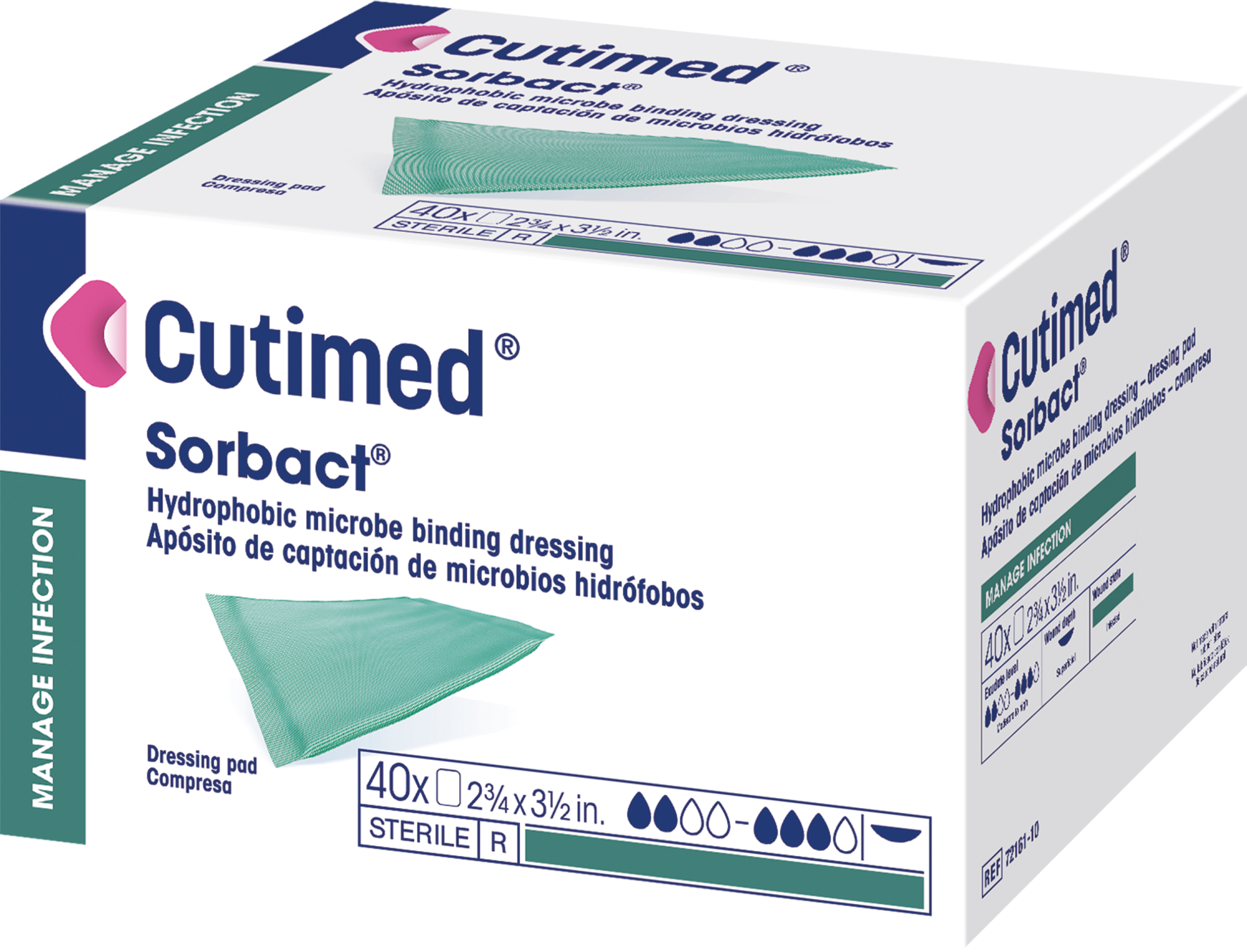
Cutimed® Sorbact® Dressing Pad
A sterile, hydrophobic bacteria binding wound dressing
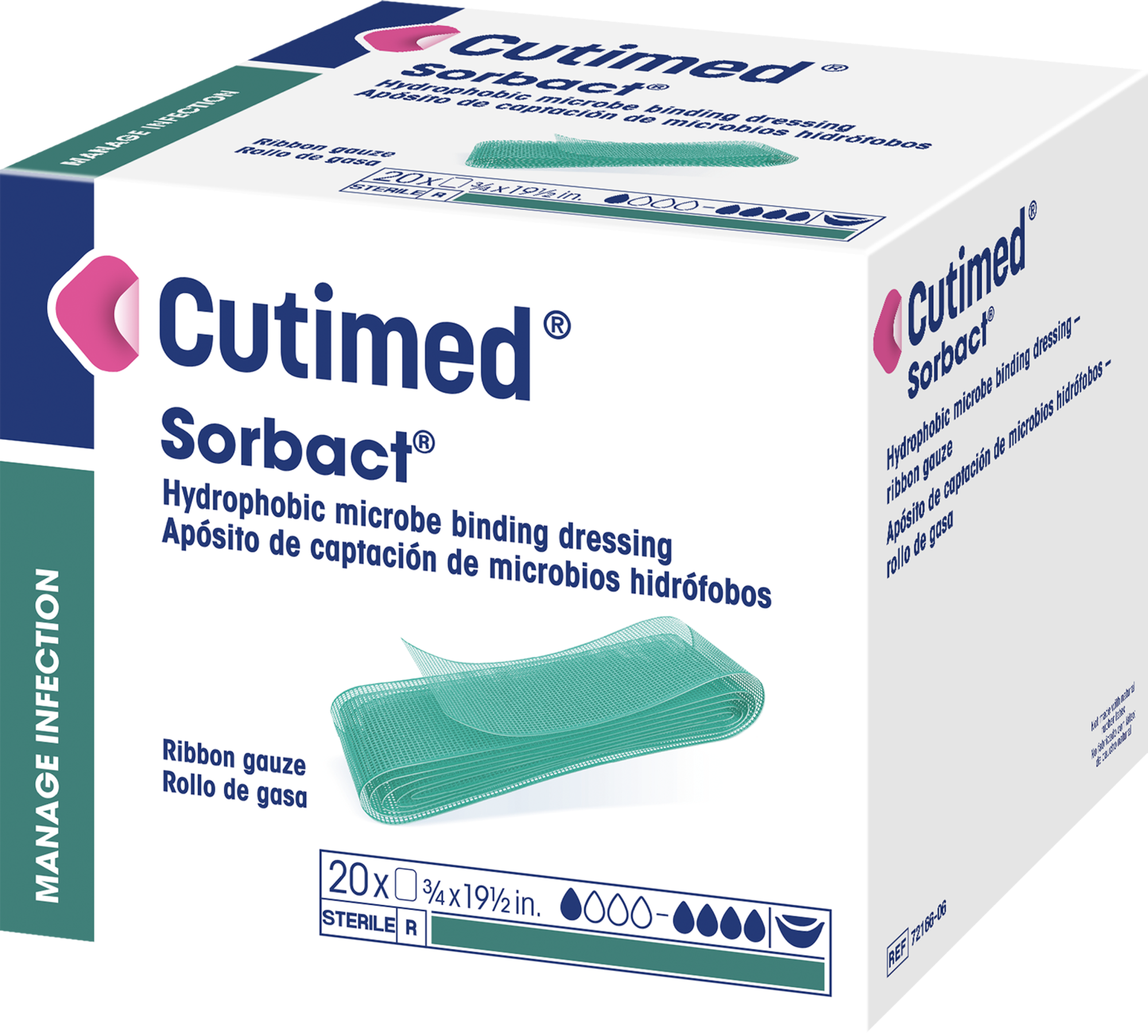
Cutimed® Sorbact® Ribbon Gauze
A sterile, hydophobic bacteria binding wound dressing
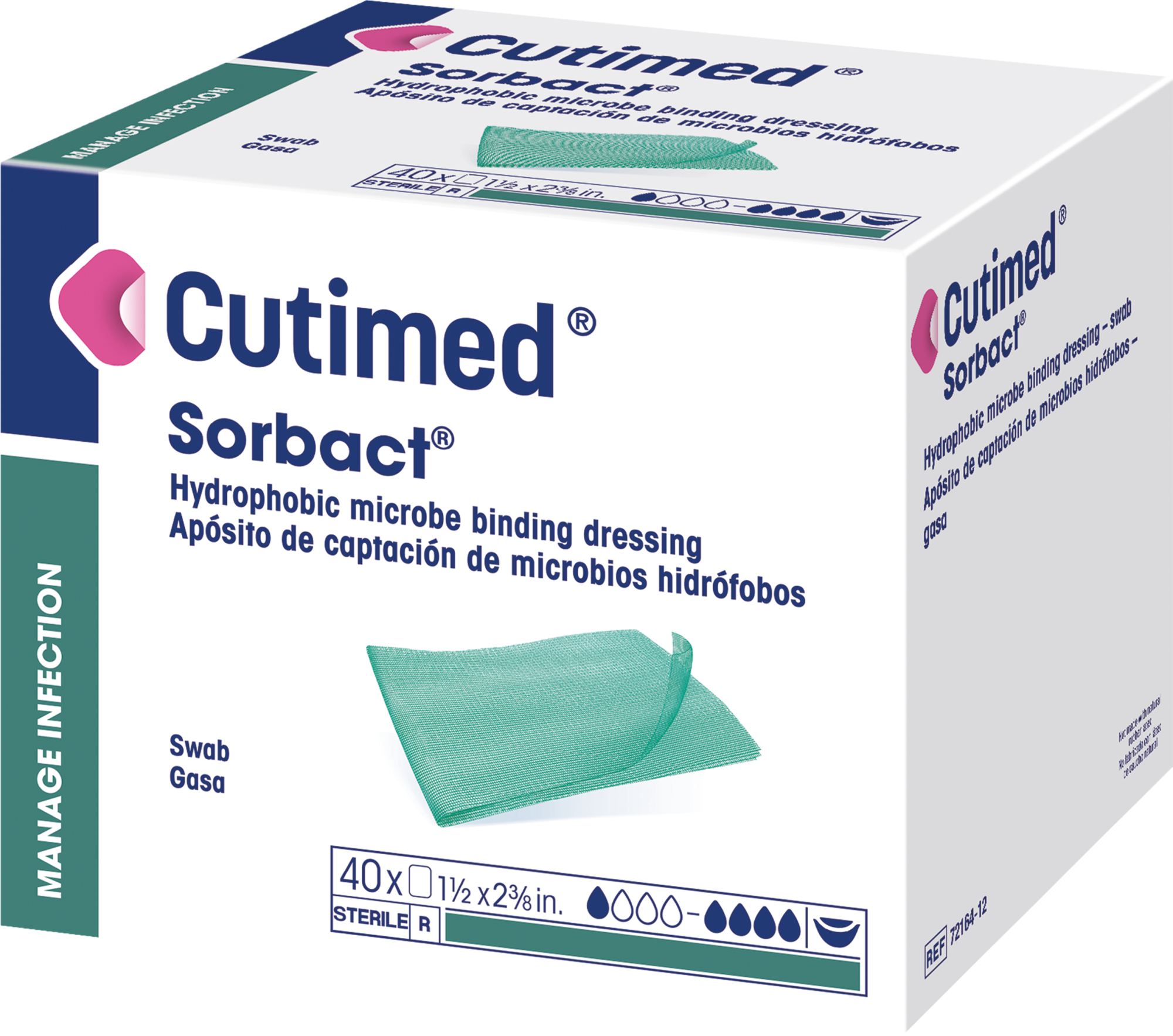
Cutimed® Sorbact® Swab
A sterile, hydrophobic bacteria binding wound dressing
Manage Infection & Exudate
Infection is the single likeliest cause of delayed healing in chronic wounds. If neglected, it may escalate to systemic infection or sepsis, which can be life-threatening. Infections can also trigger heavy exudate levels. Management and prevention of wound infection may lower the use of antibiotics and form a valuable part of your Antimicrobial Stewardship strategy. Cutimed® Sorbact® provides effective all-in-one solutions which aid in infection and exudate management to support clinical needs.
Hydrophobic bacteria binding foam dressings
Cutimed® Siltec® Sorbact® is a hydrophobic bacteria binding wound dressing, based on Sorbact® Technology, that aids in the management wound infections. The polyurethane foam absorbs and retains exudate, thereby reducing the risk of maceration and enabling a moist wound healing environment. The skin-friendly silicone adhesive borders enable atraumatic dressing changes. When the dressing is removed, microbes adhered to the dressing will be removed and development of bacterial resistance is not expected.
Cutimed® Siltec® Sorbact®
Cutimed® Siltec® Sorbact® B
A sterile, hydrophobic bacteria binding wound dressing with foam and a silicone adhesive border
Hydrophobic bacteria binding superabsorbent dressings
Cutimed® Sorbion® Sorbact® is a hydrophobic bacteria binding wound dressing, based on Sorbact® Technology, that aids in the management of wound infections. The superabsorbent core of Cutimed® Sorbion® Sorbact® absorbs and retains high levels of exudate, thereby reducing the potential risk of skin maceration. When the dressing is removed, bacteria bound to the dressing will be removed and development of bacterial resistance is not expected.
Cutimed® Sorbion® Sorbact®
Cutimed® Sorbion® Sorbact®
A sterile, hydrophobic bacteria binding superabsorbent wound dressing.
Hydrophobic bacteria binding hydrogel dressings
Cutimed® Sorbact® Hydroactive is a hydrophobic bacteria binding absorbent gel dressing, based on Sorbact® Technology, that aids in the management of wound infections. The highly absorbent hydropolymer matrix manages exudate in dry to moderate exudating wounds. When the dressing is removed, bacteria bound to the dressing will be removed and development of bacterial resistance is not expected.
Cutimed® Sorbact® Hydroactive

Cutimed® Sorbact® Hydroactive B
A bacteria binding, absorbent gel dressing with an adhesive border.
Manage Exudate
Managing exudate levels of different viscosities is a big challenge when treating wounds. A delay in wound healing is just one of many problems that can occur. Cutimed® offers reliable and innovative solutions for all exudate levels, focusing on keeping a moist wound healing environment and reducing the risk of potential skin maceration – even under compression.
Foam dressings
Our two assortments Cutimed® Siltec® and Cutimed® Cavity offer a wide range of dressings, made of 100% skin-friendly polyurethan foam – for reliable exudate management from low to high absorption levels. Whereas Cavity is especially designed for deep exuding wounds, Siltec® provides various variants for different body parts to match specific needs and a good conformability.
Cutimed® Siltec®
Cutimed® Siltec® Plus
is a silicone coated, sterile, absorbent polyurethane foam dressing with a gentle but high adherence.

Cutimed® Siltec®
is a silicone coated, sterile, non-bordered, absorbent polyurethane foam dressing
Cutimed® Siltec® B
Cutimed® Siltec® B
is a bordered, silicone coated, sterile, absorbent polyurethane foam dressing
Cutimed® Siltec® Sacrum
is a bordered, silicone coated, sterile, absorbent polyurethane foam dressing with a special shape
Cutimed® Siltec® Heel 3D
Cutimed® Siltec® Heel 3D
is a self-adherent, silicone coated, sterile, absorbent polyurethane foam dressing with a specical anatomical shape and a cushioning effect
Cutimed® Siltec® Heel 2D
Cutimed® Siltec® PLUS Heel
is a gentle but high self-adherent, silicone coated, sterile, absorbent polyurethane foam dressing with a special anatomical shape and a cushioning effect
Superabsorbent dressings
Cutimed® Sorbion® has demonstrated its efficacy in the superabsorbent wound treatment category of low to excessive exuding wounds. Based on the patented Hydration Response Technology™, Cutimed® Sorbion® has set standards in modern exudate management. Outstanding absorption capacity and exudate leakage avoidance with excellent retention performance allows for the dressing to be used even under compression.
Cutimed® Sorbion® Sachet

Cutimed® Sorbion® Sachet Multi Star
is a sterile, hydroactive, gel-forming, superabsorbent wound dressing with an anatomical shape

Cutimed® Sorbion® Sachet XL
is a sterile, hydroactive, gel-forming, superabsorbent wound dressing in a special size desgined for larger wounds
Cutimed® Sorbion® Sachet S Drainage
is a sterile, hydroactive, gel-forming superabsorbent wound dressing in a special size designed for placement around exit sites of drainage tubes
Cutimed® Sorbion® Sana

Cutimed® Sorbion® Sana Gentle
is an atraumatic, sterile, hydroactive, gel-forming, superabsorbent wound dressing

Cutimed® Sorbion® Sana Multi Star
is a is an atraumatic, sterile, hydroactive, gel-forming, superabsorbent wound dressing with an anatomical shape
Cutimed® Sorbion® Border
Cutimed® Sorbion® Border
is a bordered, sterile, hydroactive, gel-forming, self-adhesive, superabsorbent wound dressing
Cutimed® Sorbion® Border Sacrum
is a bordered, sterile, hydroactive, gel-forming, superabsorbent wound dressing with a special shape
Alginate dressing
Natural fibers derived from seaweed are the basis of highly absorbent Cutimed® Alginate dressings. The alginate dressing is composed of 80% Calcium and 20% Sodium, and is a gel-forming wound dressing for non-infected wounds with a hidden integrity layer for stability under wet conditions. For this reason Cutimed® Alginate can be used for moderately to highly exuding wounds, even under compression.
Cutimed® Alginate
Cutimed® Alginate
is a sterile, non-medicated alginate dressing, consisting of mainly calcium alginate fiber
Hydrocolloid dressing
In the presence of wound exudate, the hydrocolloids in the Cutimed® Hydro dressings absorb liquid and form a gel that does not adhere to the wound. This gel forms a moist environment at the wound interface which supports the wound healing process. This also means less pain and discomfort for the patient when removing the dressing. Cutimed® Hydro dressings can manage dry to moderately exuding wounds.
Cutimed® Hydro
Cutimed® Hydro B
is a bordered, hydrocolloid dressing designed to maintain a moist wound environment.
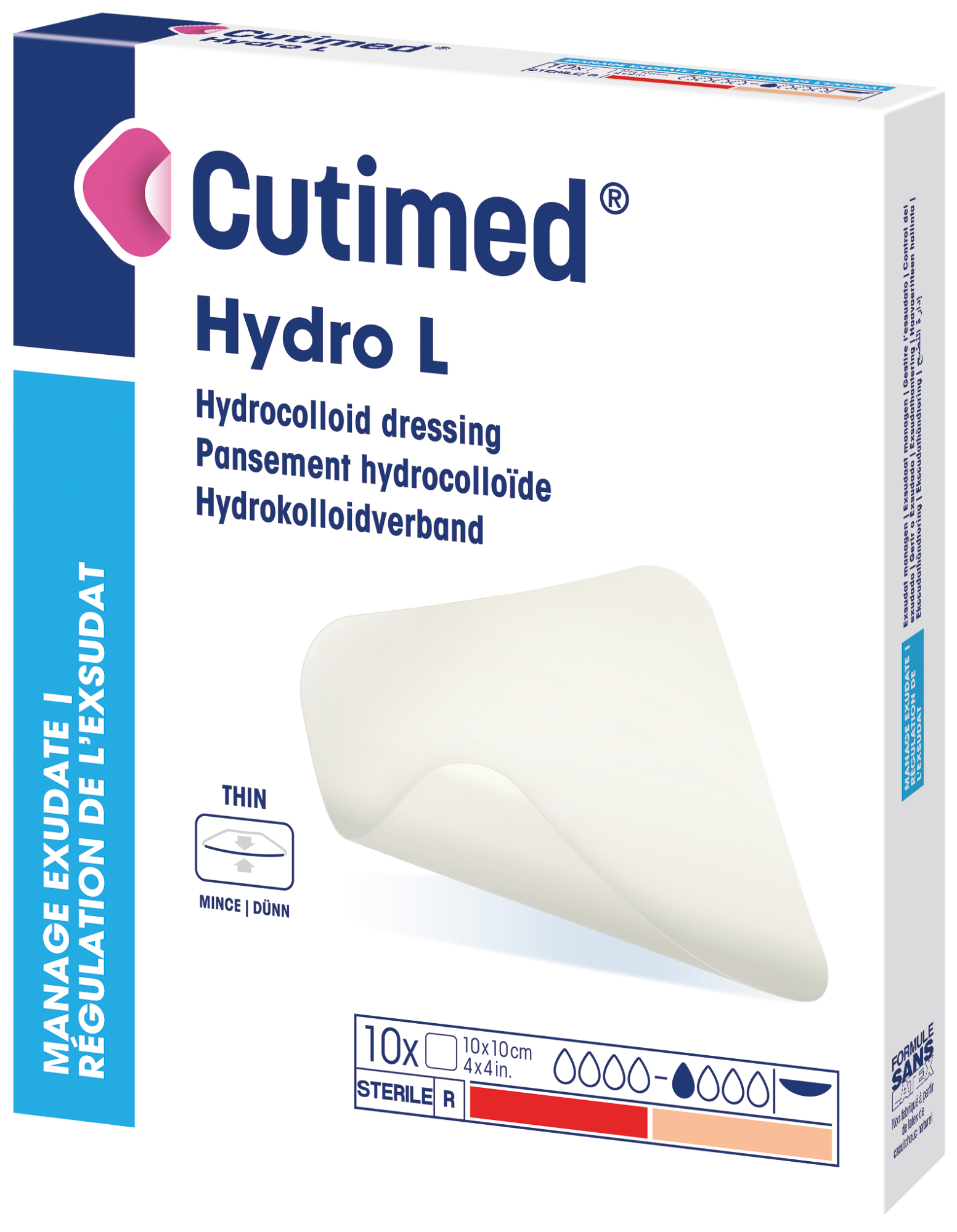
Cutimed® Hydro L
is a lite, hydrocolloid dressing designed to maintain a moist wound environment.
Manage Tissue Boost
Often times, wounds healing by secondary intention can come with clinical and economic challenges for wounds that have stalled or have not progressed towards a healing goal. Tissue boost dressings support tissue growth, accelerate healing, and contribute to early patient mobilization and reduced treatment time.
Collagen dressing
Collagen dressings with calcium alginate absorb wound moisture, forming a gel, thus maintaining a moist enviornment at the wound surface that aids in the formation of granulation tissue and epithelization.
Cutimed® Epiona

Cutimed® Epiona®
is a collagen alginate dressing that boosts wound healing
Complementary
Flexible and comprehensive product solutions are often required in wound management. Complementary products include wound contact layers and impregnated sterile dressings for atraumatic dressing changes, and skin care products. This also includes a Total Contact Cast (TCC), which is a preferred treatment for diabetic foot care according to international guidelines.
Wound contact layers
These primary wound contact layers allow for atraumatic dressing changes and promote undisturbed wound healing – due to fewer necessary dressing changes. Furthermore, Cutimed® Cuticell® Contact, with its transparent silicone coating, allows for an easy wound inspection.
Cuticell® Contact
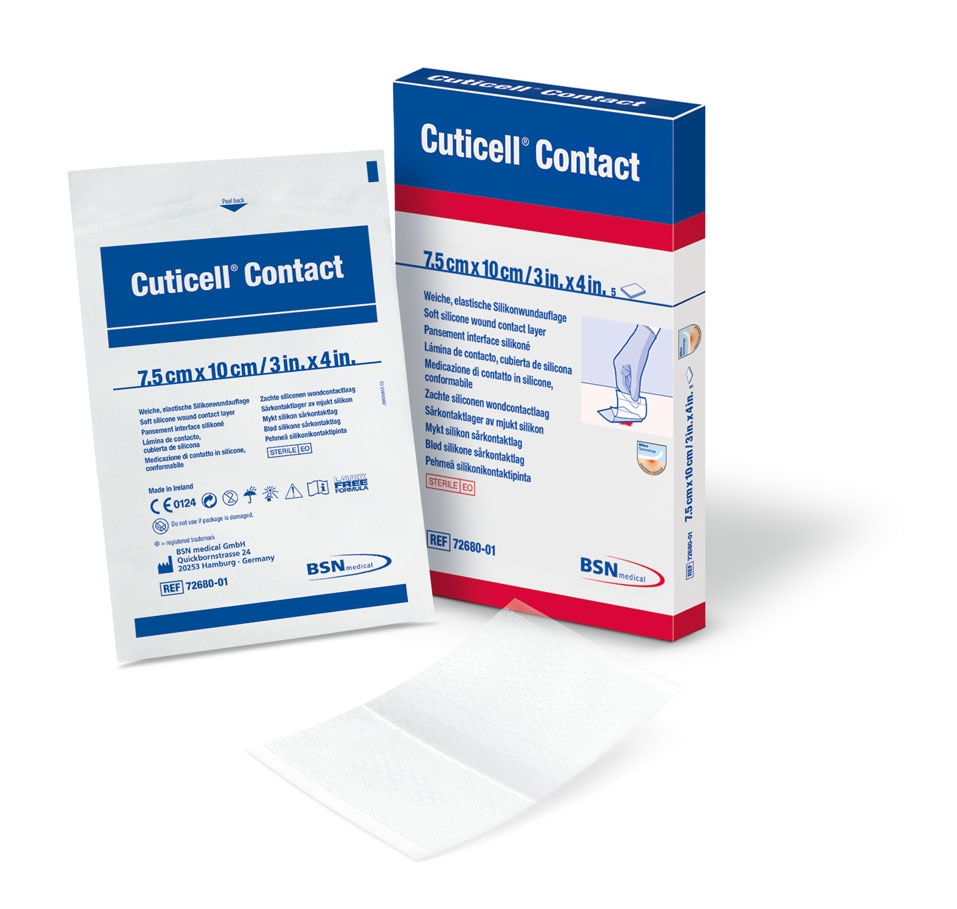
Cutimed® Cuticell® Contact
is a primary wound contact layer consisting of an elastic and transparent polyurethane film coated with soft silicone.
Ointment dressings
The open weave of these ointment dressings allows exudate to pass through into the absorbent secondary dressing and aids in atrumatic dressing changes.
Cuticell®

Cutimed® Cuticell®
is a sterile, non-medicated, low adherent dressing due to its ointment coating.
Skin care
Wound management must take skin care into consideration. Skin maceration, skin dryness or skin irritation can lead to wounds or healing complications. Skin care products can help to rebalance the moisture level in the skin or protect the skin from the damage and irritation caused by bodily fluids, such as digestive or wound fluids.
Cutimed® Protect
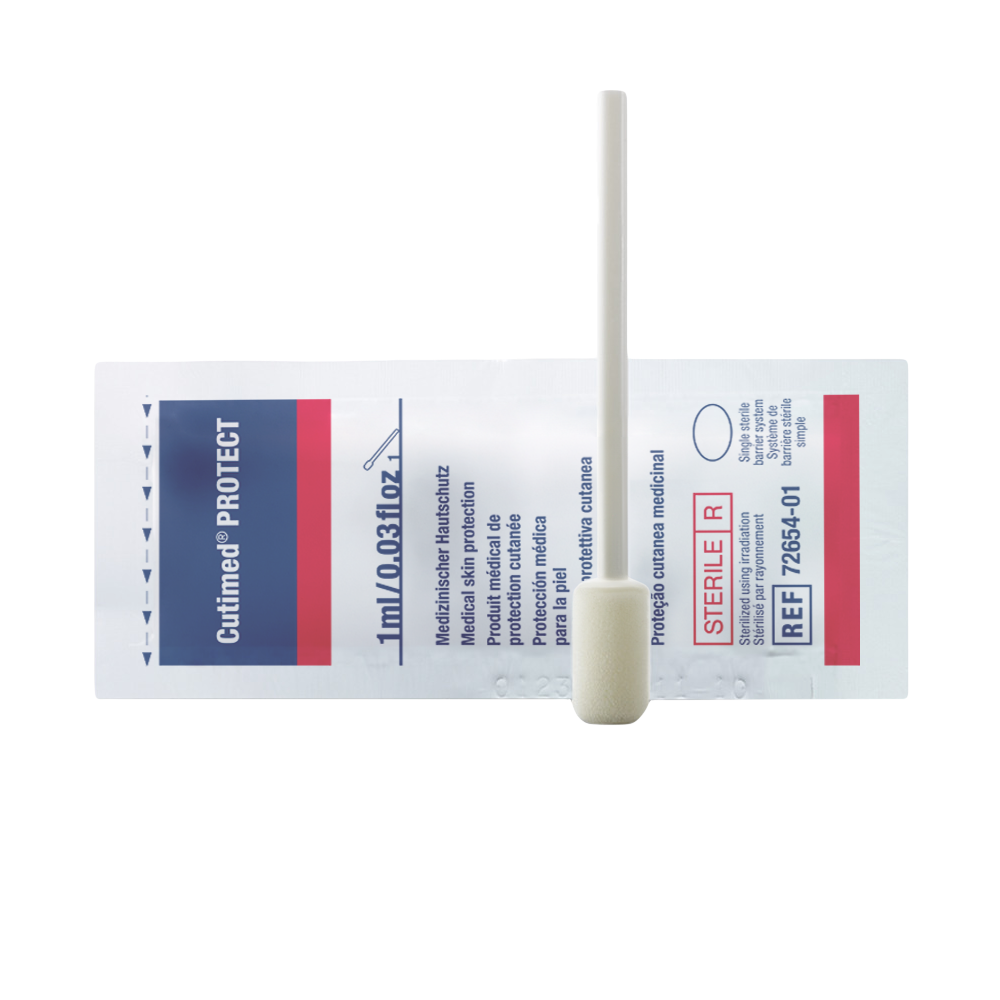
Cutimed® PROTECT | Foam Applicator
is a liquid skin protectant with a foam applicatior that forms a barrier over the skin.

Cutimed® PROTECT | Spray
is a liquid skin protectant spray that forms a barrier over the skin.
Cutimed® Acute

Cutimed® ACUTE | 10% Urea Intensive Cream Mousse
is for very high moisturizing needs; provides relief and medical skin care for very dry skin.
Total contact cast
When considering treatment for DFUs, total contact casting is considered the gold standard for offloading and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers.
Cutimed® Off-Loader Select
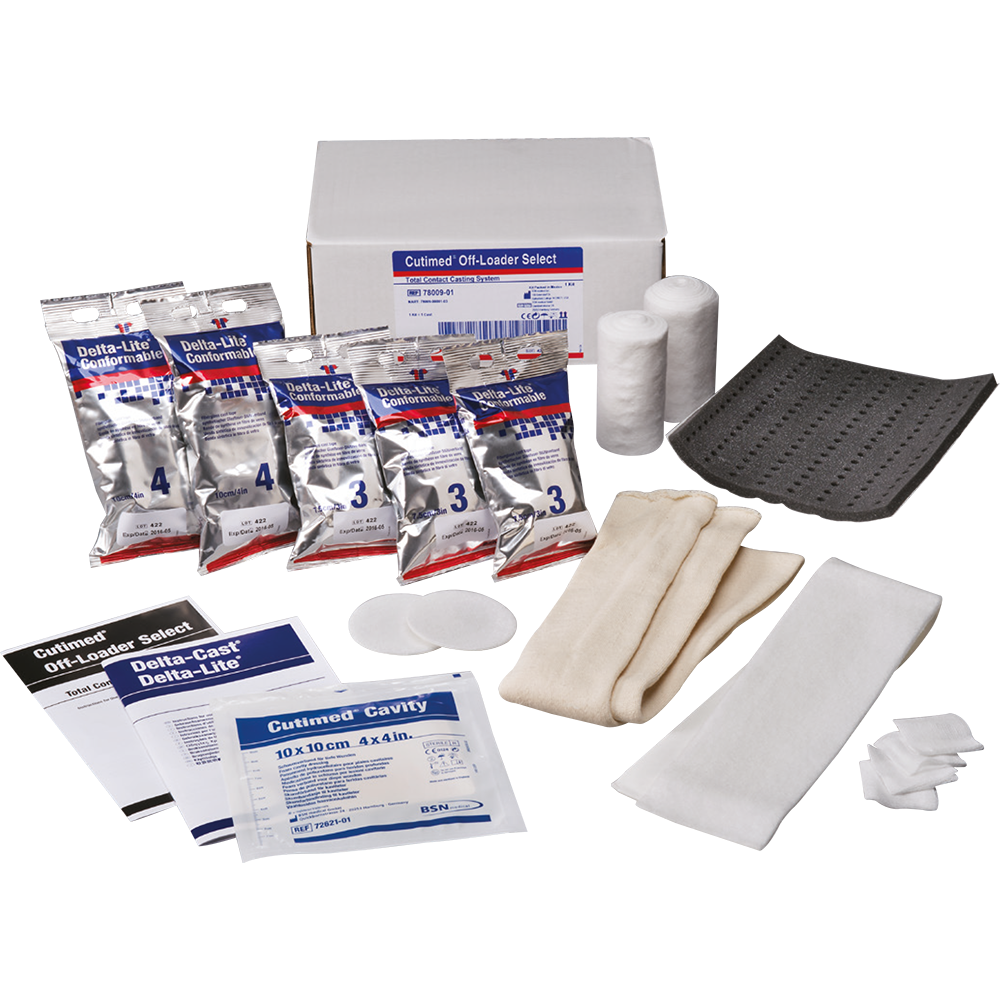

Cutimed® Off-Loader Select
is an all-in-one kit which contains the components and instructions needed to make a total contact cast.
